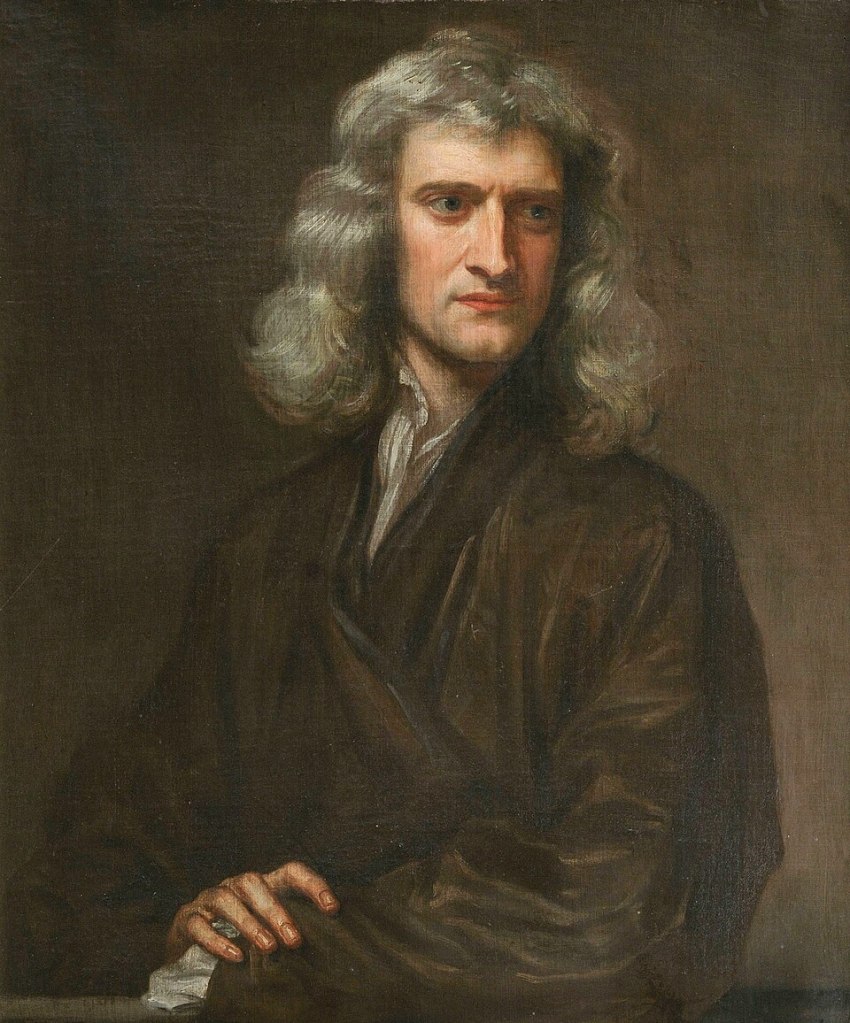
Isaac Newton (1642–1727), remembered as one of the greatest mathematicians and architect of modern physics, devoted more time to theology and biblical study than to science. Among his vast unpublished papers lies a remarkable calculation: Newton believed that the End of Times would not occur before the year 2060. His thesis was not a prediction of hell on Earth, but rather a forecast of the corrupt secular and spiritual powers giving way to the establishment of Christ’s kingdom on earth.
Newton’s notes on prophecy and chronology survive in the Yahuda manuscripts, now housed at the National Library of Israel. For more than a century, these papers were considered “unfit to print” and remained hidden in the English Earl of Portsmouth’s family archives. In 1936, Sotheby’s auctioned off Newton’s theological and alchemical writings for just over 9,000 British pounds or about $1 million in today’s dollars. Abraham Shalom Yahuda, a Jewish polymath and collector, recognized their importance and purchased a large portion, including Newton’s calculations on the End of Times.
Newton was deeply engaged with biblical prophecy, especially the Books of Daniel and Revelation. He believed these texts contained coded timelines of history on into the future. In Observations upon the Prophecies of Daniel (published posthumously in 1733), he wrote: “The prophecies of Daniel are all of them related to one another, as if they were but several parts of one general prophecy… The Apocalypse of John is written in the same style and language with Daniel, and hath many of the same figures.”
In Daniel 7:25 and 12:7, and again in Revelation 12:14, “a time” is taken as one year, “times” as two years, and “half a time” as half a year—an interpretation rooted in the Aramaic/Hebrew idiom in which “time” means “year.” Revelation 11:2 and 13:5 describe the same period as 42 months, which equals 3½ years (42 ÷ 12). Revelation 11:3 and 12:6 express it again as 1,260 days, using the Jewish symbolic 360‑day prophetic year (360 × 3.5 = 1,260). Across Revelation 11–13, these expressions appear interchangeably, reinforcing the equivalence.
The 3½‑year duration itself is symbolic: it is half of seven, the biblical number of completeness, and thus represents a period of incompleteness or tribulation deliberately cut short. Cut short because in Matthew 24:22 Jesus states, “Unless those days had been cut short, no flesh would be saved; but for the sake of the elect those days will be cut short.” A full seven would symbolize evil completing its course, but Scripture portrays God as limiting evil’s duration, preserving a some but not all, and interrupting the “full seven” before it reaches completion.
Later interpreters extended this further. Drawing on Numbers 14:34: “a day for a year”; and Ezekiel 4:6, where God again assigns “a day for a year,” they applied the day‑year principle to the 1,260 days, transforming them into 1,260 years.
Newton then sought a historical anchor, a year to start the clock to End Times. He identified 800 AD, when Charlemagne was crowned Emperor of the Romans by Pope Leo III, as the beginning of ecclesiastical corruption. For Newton, this coronation marked the fusion of secular and papal power: the fulfillment of Daniel’s prophecy of a blasphemous authority ruling over the saints. Adding 1,260 years to 800 AD produced the year 2060. In his notes, Newton wrote: “The period of 1260 days, if dated from the complete conquest of the three kings A.C. 800, will end A.C. 2060.” (Newton preferred A.C., Anno Christi, in the year of Christ over A.D., Anno Domini, in the year of the Lord.)
Newton also considered 2034 as an alternative. Anchoring the calculation in 774 AD; the year of Charlemagne’s conquest of the Lombards and alliance with Pope Adrian I: 774 plus 1260 equals 2034. The year 774 also coincided with a massive solar storm, sometimes referred to as the Charlemagne Event (stronger than the Carrington Event of 1859), with auroras reaching deep into southern latitudes and temperatures dropping a few degrees. Yet 2060 remained the most consistent date in his manuscripts.
Newton believed that the corrupt powers that would bring about the End of Times was both the papacy and the secular rulers who supported the church. In his manuscripts he clearly identified the papacy as the “little horn” and the “man of sin,” a corrupt ecclesiastical power that had usurped apostolic Christianity. At the same time he perceived that secular rulers were equally part of the apostate system destined to collapse. The ten horns of the Beast were the European kingdoms. Their political power upheld the papal system and thus shared in its guilt and its eschatological fate.
Importantly, Newton did not envision annihilation at the End of Times. He saw 2060 as the end of corruption and the dawn of a new divine order. He cautioned it may end later, but said “I see no reason for its ending sooner. This I mention not to assert when the time of the end shall be, but to put a stop to the rash conjectures of fanciful men…”
Newton feared that false predictions would undermine faith. His calculation was meant as sober interpretation, not sensational prophecy. He emphasized that only God knows the appointed time: “It is not for us to know the times and seasons which God hath put into his own breast.”
Newton’s calculation of the End of Times flows logically from the biblical text, and he treats the prophetic numbers with strict literalism. Yet he interprets the tribulation not as a final, catastrophic episode at the end of history, but as a long historical decline. Slow corruption within secular and ecclesiastical institutions. All culminating in the restoration of true Christianity.
Although Newton’s prophetic writings remained unpublished during his lifetime, the rediscovery of the Yahuda manuscripts in the 1930s revealed the full scope of his vision. He saw the End Times not as annihilation but as transformation: the fall of apostate Christianity, the renewal of true religion, and the establishment of Christ’s kingdom of peace.
Newton’s restrained timing aligns with Christ’s teaching in Matthew 24:36: “But of that day and hour no one knoweth, not the angels of heaven, but the Father alone.” In Christian eschatology, the Second Coming is likened to a Canaanite or Jewish wedding: the Father alone knows the day, the Son prepares a place, and the bride: the Church, must remain watchful. Newton’s calculations were an attempt to glimpse the architecture of prophecy, yet he humbly accepted the unknowable will of God.
Graphic: Isaac Newton by Godrey Kneller, 1689. Issac Newton Institute. Public Domain.