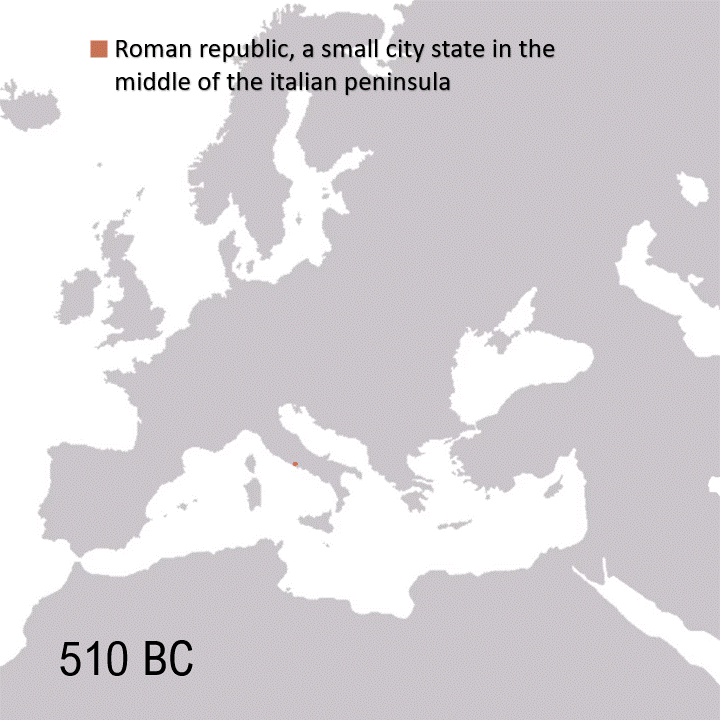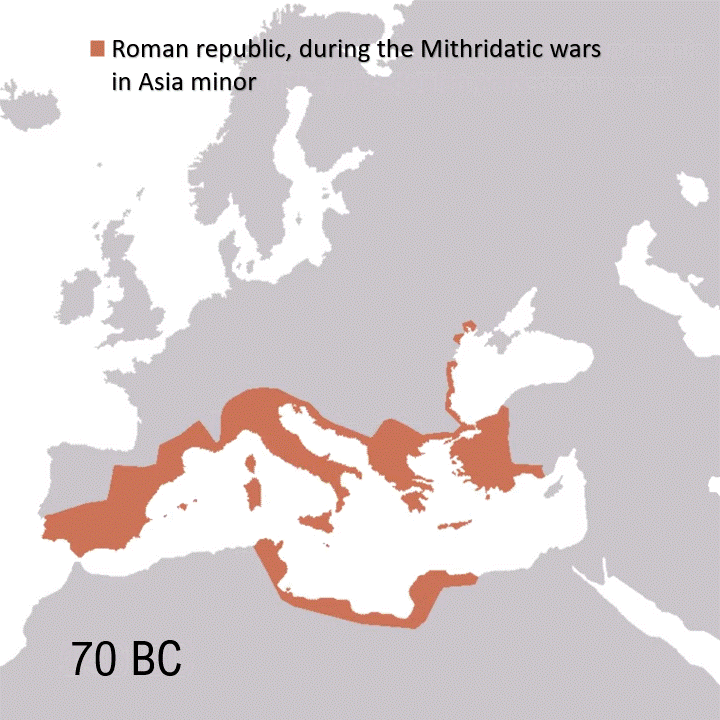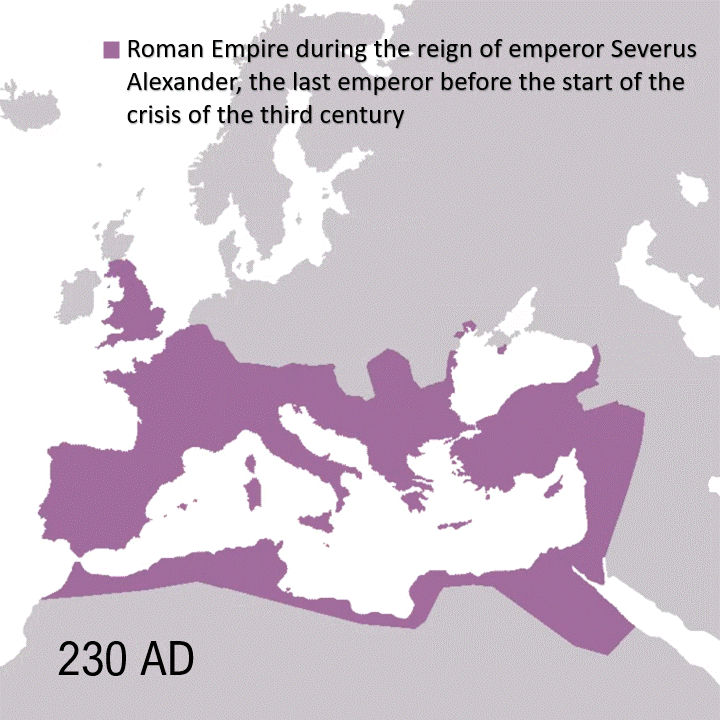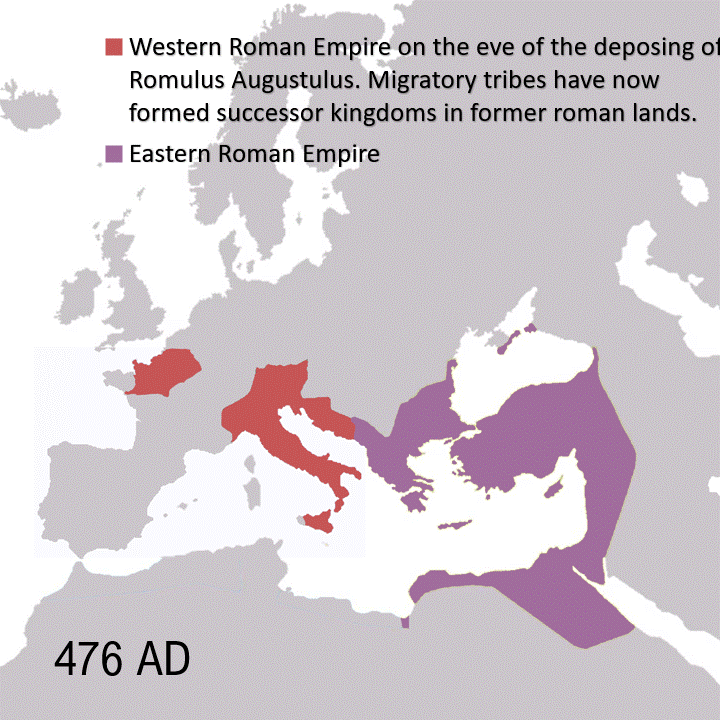
The Peloponnesian War, fought over 27 years (431-404 BC), cost the ancient Greek world nearly everything. War deaths alone approached 8-10 percent of their population: up to 200,000 deaths from battle and plague. The conflict engulfed nearly all of Greece, from the mainland to the Aegean islands, Asia Minor and Sicily. Though Sparta and its allies, in the end, claimed a tactical victory, the war left Greece as a shadow of its former self.
The Golden Age of Athens came to an end. Athenian democracy was replaced, briefly, by the Thirty Tyrants. Sparta, unwilling to jettison its insular oligarchy, failed to adapt to imperial governance, naval power, or diplomatic nuance. Within a generation Sparta was a relic of history. First challenged by former allies in the Corinthian War, then shattered by Thebes, which stripped the martial city-state of its aura of invincibility along with its helot slave labor base: the economic foundation of Sparta. Another generation later, Macedon under Philip II and Alexander the Great finished off Greek dominance of the Mediterranean. After Alexander’s death in 323 BC, Rome gradually absorbed all the fractured pieces. Proving again, building an empire is easier than keeping one.
Thucydides, heir to the world’s first historian: Herodotus, reduced the origins of the Peloponnesian War to a primal emotion: fear. In Book I of his History of the Peloponnesian War he writes: “The growth of the power of Athens, and the alarm which this inspired in Sparta, made war inevitable.” Athens had violated trade terms under the Megarian Decree with a minor Spartan ally but that was pretext, not cause. Sparta did not go to war over market access. It went to war over fear. Fear of what Athens had become and a future that armies and treaties may not contain.
War and fear go together like flame to fuse. Sparta went to war not for fear of a foe, Sparta knew no such people. It was not fear of an unknown warrior, nor fear of battlefields yet to be choregraphed, but fear of an idea: democracy maintained and backed by Athenian power. And perhaps, more hauntingly precise, fear of itself. Not that it feared it was weak but of what it may become. They feared no sword or spear, their discipline reigned supreme against flesh and blood. Yet no formation, no stratagem, no tactic of war could bring down a simple Athenian belief: the rule of the many, an idea anathema, heretical even, to the Spartan way of life.
So, they marched to war, not to defeat an idea but to silence the source. Not to avenge past aggression but to stop a future annexation. They won battles, small and large. They razed cities. But they only destroyed men. The idea survived. It survived in fragments, bits here, bits there, across time and memory. What it did kill, though, was the spirit of Athens, the Golden Age of Athens. But the idea that was Athens lived on across space and time: chiseled into republics that rose from its ashes and ruins.
The radiance of Athens dimmed to shadow. Socrates became inconvenient. Theater became therapy; a palliative smothering of a cultural surrender. And so, civilization moved to Rome.
Source: A War Like No Other by Victor Davis Hanson, 2005. History of the Peloponnesian War by Thucydides, Translated by Richard Crawley, 2021. Graphic: Syracuse vs Athens Naval Battle. CoPilot.