On 16 January 27 BC, the Roman Senate voted to confer the title of Augustus upon Octavian, Julius Caesar’s adopted son, realistically marking the end of the Roman Republic and the beginning of the Roman Empire. This decision aimed to restore stability and order after years of civil war and internal conflict, legitimizing Octavian’s authority while maintaining a veneer of republican governance. Augustus took effective control of the military, religion, bureaucracy, and administrative operations of the empire.
After the assassination of Julius Caesar in 44 BC, Octavian, in 43 BC, formed the Second Triumvirate with Mark Antony and Lepidus. Following their eventual conflict and his decisive victory at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, Octavian became the uncontested ruler of Rome.
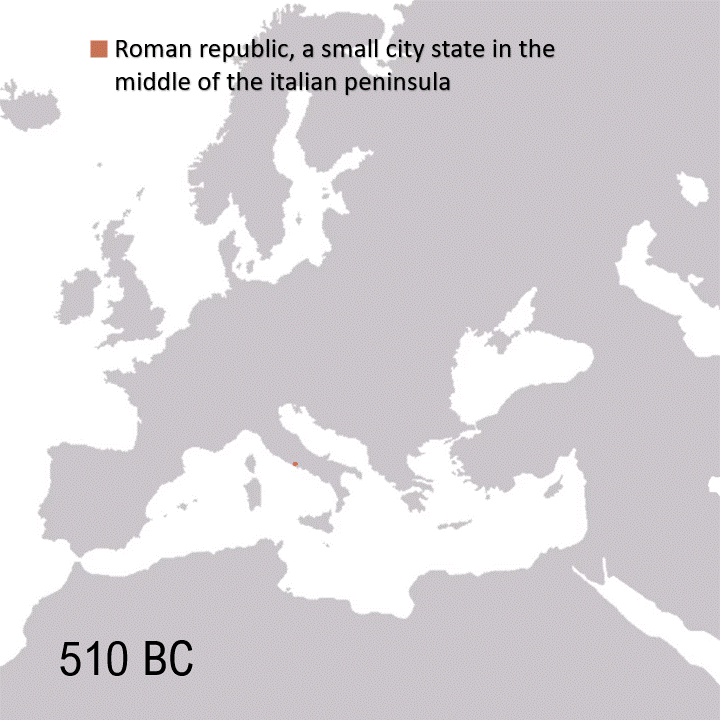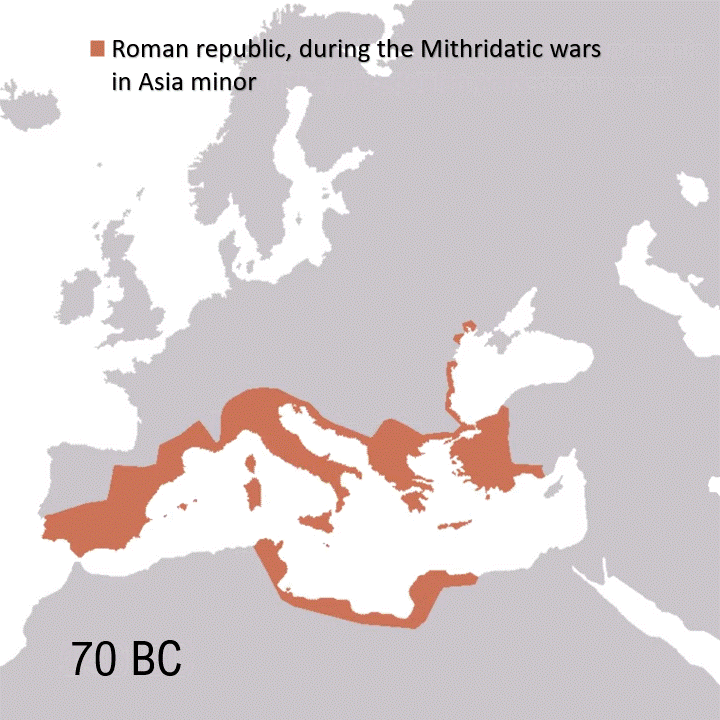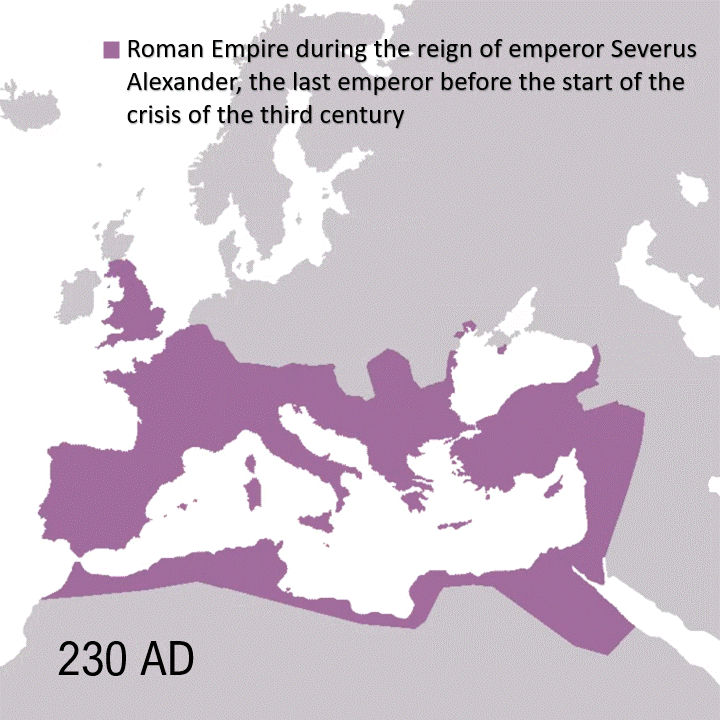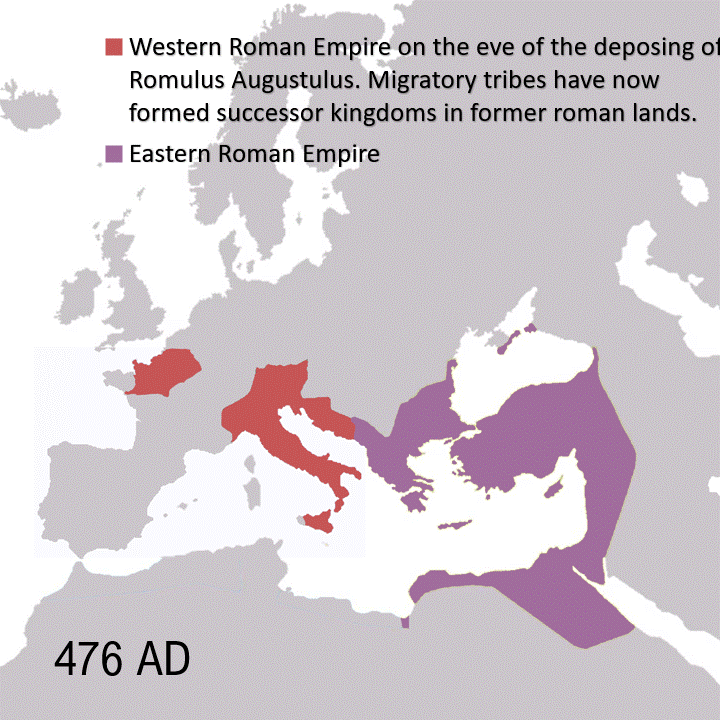
The Roman Empire was the final iteration of the Roman government, which began as a monarchy with Romulus as king in 753 BC, transitioned into a republic in 509 BC, and lasted through the era of civil wars and dictatorships until Octavian’s elevation as Augustus in 27 BC. The Roman Empire as a whole lasted until 476 AD when the Western Empire fell, while the Eastern Empire continued until 1453 AD.
Trivia: 16 January 27 BC, is the actual Julian calendar date, retained and quoted in texts for historical accuracy. According to the Gregorian calendar, however, the date marking the end of the Roman Republic would be 26,27 January 27 BC.
Source: Roman Republic…by M. Vermeulen, The Collector, 2020. Graphic: Evolution of the Roman Empire, by ESKEHL-Wikipedia, 2022.