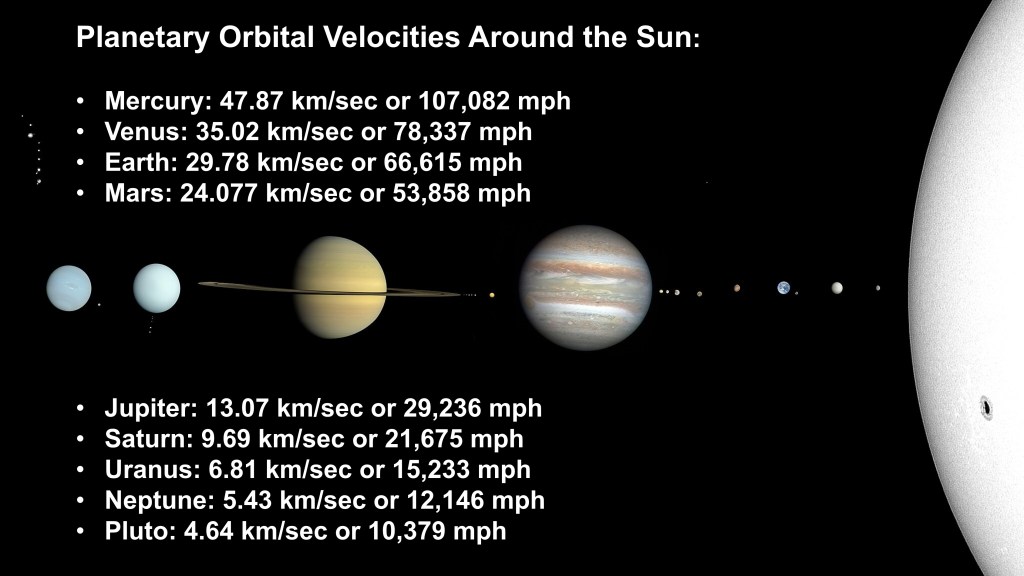
Kepler’s Second Law, first published between 1609 and 1619, describes how a planet’s orbital speed varies along its elliptical orbit around the Sun. As the planet approaches the Sun, the gravitational pull from the Sun is stronger causing the planet to move faster. As a planet moves away from the Sun it slows down.
Kepler’s Second Law in geometric jargon: A line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time.
Source: Smithsonian, How Things Fly. Graphic of the Planets and the Sun by CactiStaccingCrane 2022.