“Those who deny freedom to others deserve it not for themselves.”—Abraham Lincoln
“Whoever does not have two-thirds of his day for himself, is a slave, whatever he may be: a statesman, a businessman, an official, or a scholar.” — Friedrich Nietzsche
As the great continental glaciers receded at the end of the Pleistocene, fertile land emerged, allowing for the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture. Farming was labor-intensive, and with the rise of permanent settlements came the demand for constrained and controlled labor. Slavery, likely with first roots in Mesopotamia, though independent manifestation by the Pharaohs in ancient Egypt and other early civilizations, made it ubiquitous, and it has never disappeared.
From the bonded laborers of the Pharaohs to the structured servitude in Greece and Rome, from the transatlantic trade that brutalized African populations to the modern exploitation of migrant workers in sweatshops and the sex trades, slavery has evolved rather than vanished. Each era refines its own form of servitude; forced labor, insurmountable debt, bureaucratic entrapment, or corporate exploitation. It is a practice as ancient as prostitution and taxation, deeply embedded in human society, yet constantly shifting into less visible but equally insidious forms. As long as slavery remains profitable its existence will continue to indelibly stain humanities’ collective soul.
Slavery, and its ultimate contrast, freedom, was a persistent theme in the works of sci-fi author Robert A. Heinlein. With a piercing social awareness, Heinlein, who, in his early years, was described by Isaac Asimov as a ‘flaming liberal’—picked up the theme and horrors of slavery with his 1957 juvenile novel “Citizen of the Galaxy”; bringing the many forms of servitude into the personal history of a precocious kidnapped boy named Thorby. Citizen of the Galaxy is a planet-hopping, spacefaring critique of oppression, class structure, and the nebulous concept of freedom. Heinlein crafts a future where contrasting societies across the galaxy reflect varying degrees of servitude and autonomy, if not necessarily total freedom. Man rarely allows himself complete independence.
Heinlein through the lens of Thorby explores the various shades of slavery, beginning with the brutal, controlling enslavement and continuing to more subtle forms that the individual may not even recognize as confinement. (Partial plot giveaways beyond this point.) Escaping his initial enslavement by the graces of a kindly, strict, but loveable old cripple named Baslim, Thorby moves into a hierarchical, structured existence of spacefaring traders then onto a self-imposed, due to a thirst for justice, straitjacket of a corporate bureaucracy on his birth planet of Terra. A life story of how control can be imposed by others or by ourselves.
As Heinlein’s social perspectives evolved, his libertarian leanings took greater prominence in Citizen of the Galaxy. Through Thorby’s life journey, Heinlein emphasizes personal autonomy, resistance to tyranny, and the moral duty to fight injustice. Baslim, Thorby’s first mentor, symbolizes the idea that one person can stand against oppression and make a difference, even if it takes many miles and years to materialize.
This theme runs through much of Heinlein’s work, but here, it’s especially poignant because Thorby is powerless for much of the novel, making his eventual triumph all the more meaningful. Heinlein’s novels, Farnham’s Freehold, Friday, and Time Enough for Love, explore slavery and control, reinforcing humanity’s inherent need for freedom, or at the very least, breathing space.
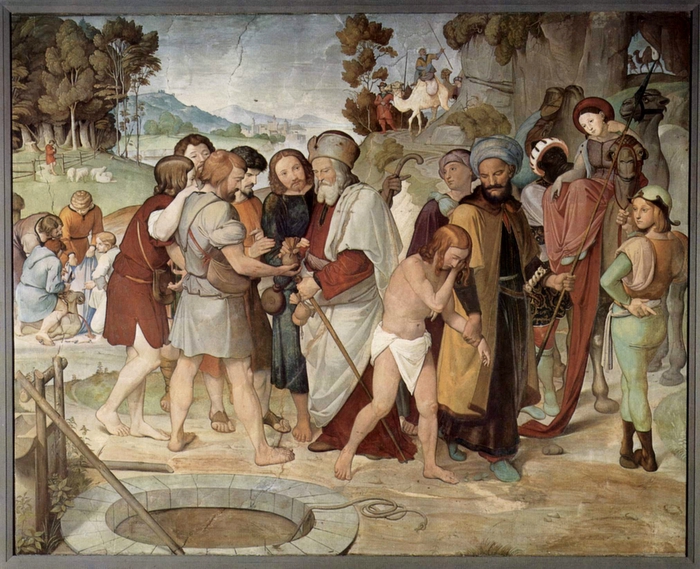
Source: Citizen of the Galaxy by Robert A. Heinlein, 1957. Graphic: Joseph Sold into Slavery by Friedrich Overbeck, 1816. Vanderbilt University. Public Domain.