Drum, a plump turkey, trusted his caring master, Strum, who fed him daily and cooed, “You’re the finest bird here.” Drum, a data geek, tracked his weight, 18 pounds on day 300, projecting 24 by day 400. On day 364, a Wednesday, he lost his head and some weight. By Thursday, day 365, Strumpf found him tasty, and his weight hit zero. Blind trust in trends can carve you up.
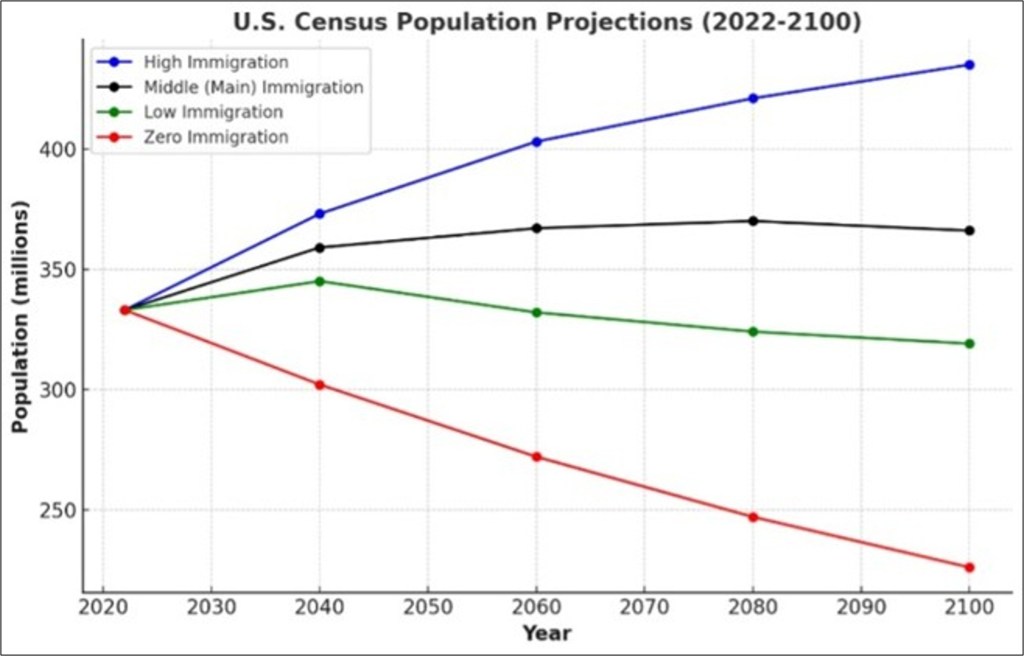
The Census Bureau’s 2023 Population Projections for the U.S. to 2100 play the same game. This “projection, not prediction” uses births (Total Fertility Rate, TFR, at 1.6), deaths, and net migration, spinning four population scenarios: Zero Immigration (333 million today drops to 226 million, down 32%), Low (down to 317 million), Main (up to 369 million), and High Immigration (435 million with 1–1.5 million newcomers yearly). Only immigration increases the population; births and deaths stay flat. It’s 78 years built on 2–3 years of data; no risks, no “what ifs,” no alternatives.
This is a house of cards sold as insight. Projections might hold up in the short term, but 78 years? Please. The Census Bureau, I assume, pitches this study for policy, budgets, districts, but it’s a narrative push: immigration or bust. Zero immigration craters us to 226 million; 1.5 million new bodies annually swells the population to 435 million. Yes, immigration boosts numbers, but why’s it the only solution? No probe into low births, no fixes beyond “import more bodies.” It’s not analysis, just bait for Congress and the public.
A growing or declining population has consequences. A 30% drop could tank GDP and programs such as Social Security. Or yield cheaper homes and a leaner U.S., like Japan (96 million by 2050, still thriving). Growth has costs too, more support for Social Security but more sprawl, maybe more crime, resource strains but the Census skips over those trade-offs. And a low TFR isn’t fate. The WWII generation raised four kids on $60,000 (adjusted) when homes were $12,700. Now we have $420,000 homes, $65,000 wages, and $10,000-per-kid childcare, maxing out affordable families at two. Inflation (2%+ since ‘71) and $36 trillion in debt, increasing by a trillion every 3 months, destroyed the dollar and concomitantly the Federal Reserve and government killed big families.
Increasing family size is a choice. Possible solutions to reverse the trend are tax credits at $5,000 per kid, or even an expanding credit for each additional child above 2, could lift TFR from 1.6 to 2.1 by 2035. That’s 700,000–1 million extra births annually within a decade, millions more Americans by 2050, no immigration spike needed. Cut housing costs by slashing senseless regs, open land to building, drop mortgage rates to 1%) and one income might work again. A declining family size is a choice, not a given.
The Census Bureau releases raw numbers, no “why,” no debate. Immigration’s one fix but not the only one. The government broke the system; it can unbreak it. Next time, Mr. Census Bureau, ask some questions, beyond just slinging spurious stats to support a preferred narrative.
Source: Census Bureau, The Black Swan, Fable of the Bees. Graphic: Population Projections by the Census Bureau.
