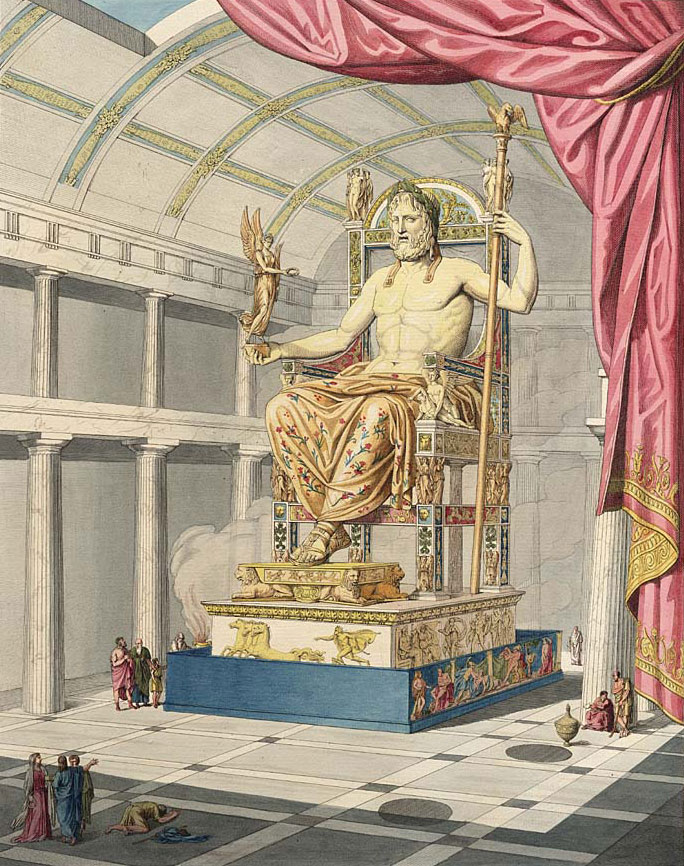
The 40’ tall statue, considered one of the seven wonders of the ancient world, was constructed by the Greek sculptor Phidias around 435 BC during the Golden Age of Athens and the time of Pericles.
The statue was composed of what the ancients called ‘chryselephantine’ or ivory, depicting flesh, and gold, which defined Zeus’ robes and ornaments. The ornaments included his scepter in his left hand and in his right hand he held a statue of Nike, Greek goddess of victory (Bulfinch reverses the hand order in his book on Greek mythology). He is seated on a throne of cedar encrusted with gold and precious stones.
Detailed descriptions of the statue come from the Greek geographer Pausanias and from numerous Greek and Roman coins and engraved gems.
The statue was housed in the Temple of Zeus at Olympia near the western coast of the Peloponnese peninsula and hasn’t been seen since the 5th or 6th century AD. It is believed to have been destroyed by an earthquake and or fire at Temple of Zeus or it was transported to Constantinople and destroyed by a fire there in 474 AD.
Source: Bulfinch’s Mythology edited by Richard Martin, 1991. Statue of Zeus by Britannica, 2024. Graphic: Olympian Zeus Statue as drawn by de Quincy, 1815, Public Domain.
